

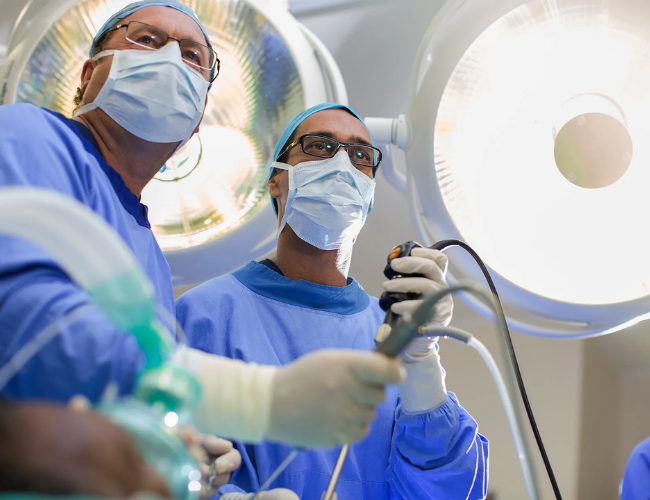
At R.P.S. Hospital, our Laparoscopic Surgery Unit is led by the Best Laparoscopic Surgeon in Ranchi, offering advanced, minimally invasive procedures designed to reduce pain, minimize scarring, and promote faster recovery. Using high-definition imaging systems and precision surgical instruments, our specialists ensure accurate diagnosis and superior surgical outcomes with enhanced patient comfort.
Recognized among the Best Doctors for Laparoscopic Surgery in Ranchi, our expert surgical team performs a wide range of laparoscopic procedures through small incisions, ensuring safety, efficiency, and minimal post-operative complications. With a strong focus on innovation, patient safety, and personalized care, R.P.S. Hospital has become a trusted destination for advanced laparoscopic surgeries in the region.
Minimally Invasive Procedures: Performed through tiny incisions, reducing post-operative pain and recovery time significantly.
High-Definition Imaging Systems: Advanced laparoscopic cameras provide crystal-clear visuals for precise surgical control.
Expert Surgical Team:Led by skilled and experienced laparoscopic surgeons trained in the latest techniques.
Faster Recovery & Shorter Stay: Most patients experience quicker healing and can return to normal life much sooner.
Comprehensive Range of Surgeries: Includes gallbladder, appendix, hernia, colorectal, and gynecological procedures, among others.
Infection Control & Safety: Strict infection control protocols and sterile procedures are followed to maintain a safe and hygienic environment for patients.
At R.P.S. Hospital, we specialize in minimally invasive laparoscopic procedures that combine precision, safety, and comfort. Our expert surgeons use advanced imaging and technology to perform surgeries with smaller incisions, less pain, and quicker recovery — ensuring the best outcomes with the least disruption to your life.
Copyright © 2025 R.P.S. Hospital | All Rights Reserved